

These processes are also used to convert staight-chain hydrocarbons to hydrocarbons which are much more useful to make chemicals which are then used to make a huge range of compounds from polymers to pharmaceuticals. The octane rating of petrols usually available for cars range from 95 upwards and contain a mixture of straight-chain, branched, cyclic and aromatic hydrocarbons, produced by the processes described below. A rating of 95 does not mean that the petrol contains just iso-octane and heptane in these proportions, but that it has the same tendency to knock as this mixture.

Thus a petrol with the same knocking characteristics as a mixture of 95% 2,2,4-trimethylpentane and 5% heptane has an octane rating of 95. The octane rating is on a scale where heptane is given an arbitary score of 0 and 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (iso-octane) one of 100. The higher the number, the less likely is a fuel to pre-ignite. The resistance of petrol to knock is measured in terms of an octane rating (octane number).
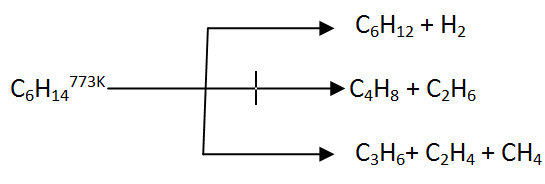
#Cracking of dodecane to make ethene series#
However, branched-chain alkanes, cycloalkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons are much more resistant to knock and straight-chain alkanes are converted into them in a series of processes in the refinery which are described in this unit. Severe knock can cause serious engine damage. The term knock is used as pre-ignition can be heard. This problem of premature ignition is referred to as pre-ignition and also as engine knock. Ideally, the mixture of petrol vapour and air is ignited with a spark at a predetermined position of the piston in the cylinder. Petrol containing a high proportion of straight chain alkanes tends to ignite in the cylinder of the car engine as the piston increases the pressure and before the cylinder reaches the optimum position. However, if this mixture is used as petrol, it does serious damage to a car's engine. The mixture of C 5-C 10 hydrocarbons obtained directly from the distillation of crude oil contains a high proprtion of straight-chain alkanes. Petrol (gasoline) contains a mixture of hydrocarbons, with 5 to 10 carbon atoms. Naphtha is the feedstock and the main products are ethene and propene, used to make polymers. The steam crackers alone occupy 64 000 m 2, which is about the size of 13 football fields. The whole site is the largest continuous chemical site in the world. These are treated in several ways including cracking, isomerisation and reforming.įigure 1 A view of the steam crackers at Ludwigshafen in Germany.
The most valuable fractions for the chemical industry, and for producing petrol, are liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), naphtha, kerosine and gas oil. Thus the various fractions obtained from the distillation of crude oil and the associated gases have to be treated further in oil refineries to make them useful. Most of these are straight chain, saturated hydrocarbons which, except for burning, have relatively little direct use in the chemical industry or as fuel for cars. Oil, and the gases associated with it, consists of a mixture of hundreds of different hydrocarbons, containing any number of carbon atoms from one to over a hundred. We depend largely on crude, the gases associated with it and natural gas (mainly methane) as the source of liquid fuels (petrol, diesel) and the feedstock for the chemical industry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
